PHOSPHATE
Phosphates, the naturally occurring form of the element phosphorus, are found in various minerals. These minerals constitute the raw material for phosphate beneficiation.
Within the phosphate matrix, we encounter:
• Phosphatic Minerals: These contain the valuable phosphorus compounds essential for fertilizer production.
• Clay Minerals: Often present as impurities and can affect the beneficiation process as it coats the phosphate minerals and increase reagent consumption
• Quartz (Sand): Quartz particles, which due to its lack of fatty acid reagents absorption is difficult to float, are common in phosphate ores.
https://www.mdpi.com/2075-163X/10/12/1109
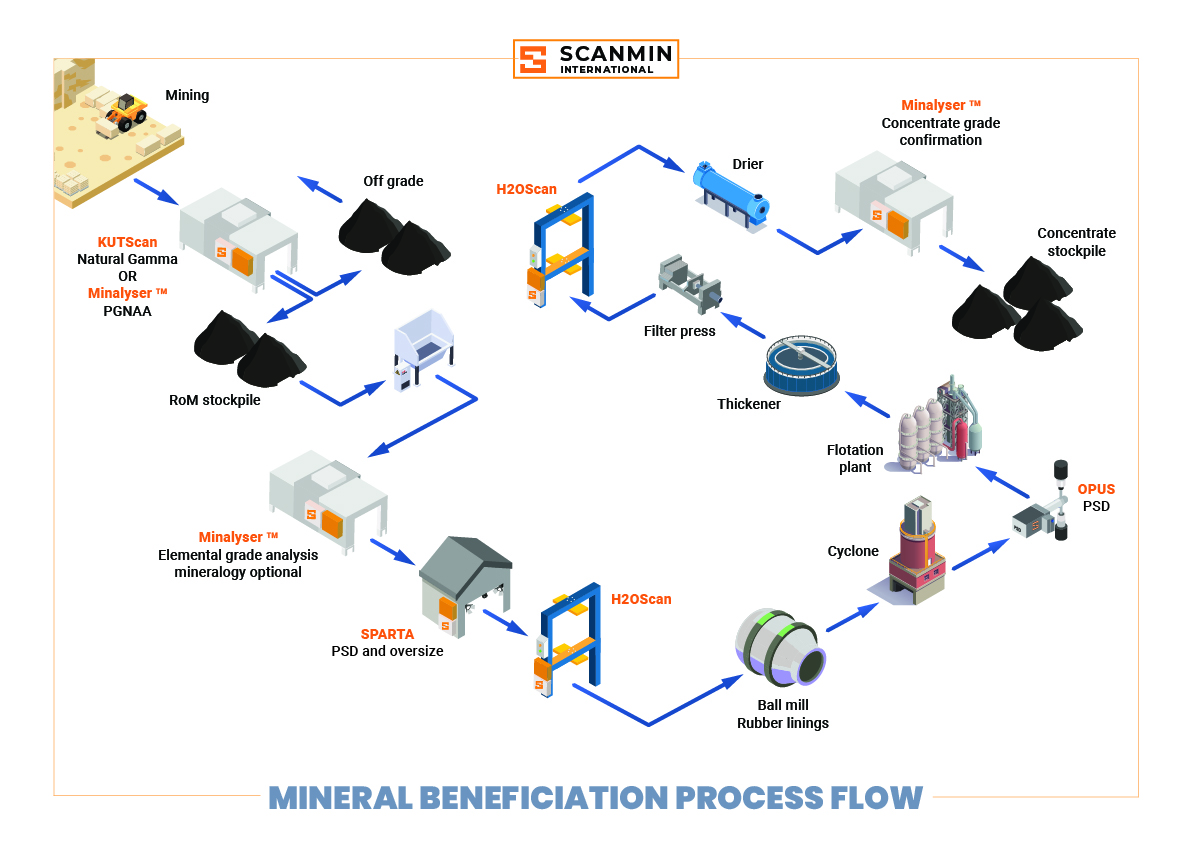
Gamma Activation Dual Response Analysis (GADRA) provide valuable online real-time measurement of all the material that assist in measurement of both phosphate and Gangue analytes.
Understanding the concentrations of these allow proper control and optimisation of downstream separations techniques
Unlike XRF and LIBS, GADRA measures all the material and is unaffected by changes in PSD, liberation, layering or restricted to a small surface measurement only.
GADRA can also measure light elements, which may present challenges for XRF equipment using silicone drift detectors
GADRA measures key elements, including phosphorus (P), calcium (Ca), and trace elements.
These measurements guide process optimization.
Specific Measurements may include:
• Phosphorus Content: Crucial for efficient phosphate recovery.
• Calcium Content: Influences gangue removal (unwanted minerals).
• Impurities e.g. iron, manganese, or magnesium
GADRA online data allow operators or automated systems in feed forward or feedback control to adjust reagent dosages and separation techniques.
PSD Measurement with an Sympatec OPUS Slurry Analyser monitor mill and grinding efficiency and ensure optimum particle size consistency for flotation
This fine-tuning enhances both recovery and grade.
Phosphate deposits may contain naturally occurring heavy metals. Mining operations that process phosphate rock can leave tailings piles with elevated levels of cadmium, lead, nickel, copper, chromium, and uranium.
Using a KUTScan Analyzer , Scanmin can measures the natural radioactivity of potassium (K), uranium (U), and thorium (Th)
The information can be used to determine safe levels of these radioactive elements.
In many situations, correlations between these elements and analytes of interest exists. Measurement of the naturally radio active elements, then provide a high confidence prediction of the analytes of interest.
Commonly occurring examples of this includes associations between
1. Uranium and Gold
2. Uranium and phosphate
3. Potassium and Phlogopite ( a gangue mineral)